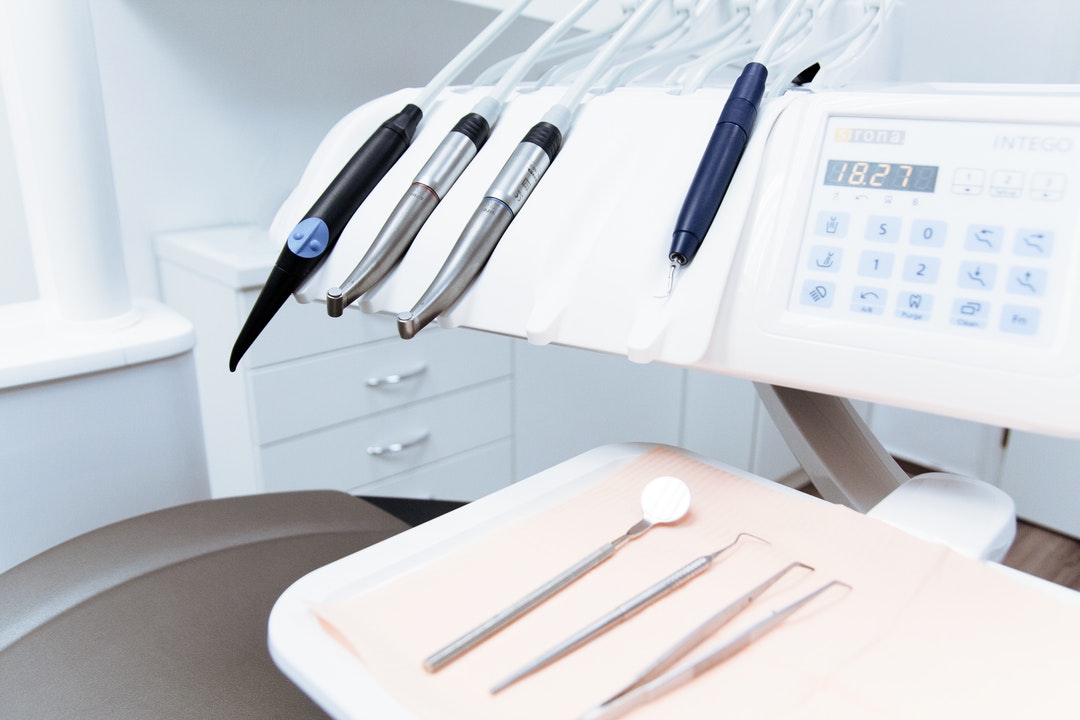
The Dental Handpiece: Continues to Impact Everyday Practice
The handpiece (coxodental handpiece) is an essential element in any dentist’s
armamentarium. It is a fundamental device that can enhance—or hinder, depending
on its efficiency and maintenance—the daily routine of a practice. Selecting
the right handpiece is critical to helping ensure the smooth operation of
everyday activities. The two primary types of handpieces—air-driven and
electric—have unique characteristics with specific benefits and drawbacks. Both
can achieve excellent results, therefore it is important to understand the
differences and advantages of each.
Impact of the Air-Driven Handpiece
Innovations come and go in dentistry, with
some being more impactful than others. The introduction of the air-driven
handpiece nearly 60 years ago has proven to be a revolutionary advancement that
genuinely changed the way dentists prepare teeth to receive dental restorative
materials. The use of air-driven “high-speed” handpieces enabled clinicians to
work more expeditiously with reduced trauma to the tooth and the patient. This
development presented a major improvement from the “belt-driven” handpieces
that preceded them and represents one of the most significant leaps forward in
the era of modern dentistry.
Since it was introduced in 1957 by Dr. John
Borden and DENTSPLY, several notable improvements have been made to the
high-speed handpiece to make the design more ergonomic, the heads smaller for
easier patient access, the turbines quieter, and bur-changing easier. Low-speed
handpieces are now reserved primarily for finishing and polishing procedures,
prophylaxis, and laboratory applications. Most dental delivery units contain
both a high- and low-speed handpiece to provide the dentist with an instrument
whose speed is specific to the operation that is being performed.
Clinical Benefits of Electric Handpieces
Electric handpieces (with variable
revolutions per minute [RPM]) are also available that give dentists added
benefits when compared to their traditional air-driven counterparts. One
significant difference is having a specific RPM, with constant torque and less
“bur chatter” (more concentric), so that when polishing or cutting through
various types of tooth structure or restorative materials, the bur does not
“bog down” or slow down when performing the clinical task. In many clinical
situations, an electric handpiece can perform the same functions that both an
air-driven high-speed and separate low-speed unit can. Since most clinicians
still prefer individual handpieces for high and low speeds so they can be more
efficient chairside, this may not make a difference when choosing between the
two systems; however, the higher initial investment for electric handpieces may
be a consideration for some clinicians. Also, given the ability to “dial in”
the desired RPM and use different contra-angles that have different gearing
ratios, the electric handpiece can be custom-tailored to perform many other
types of clinical procedures such as rotary endodontics, implant placement, and
third molar removal (via tooth sectioning), for example. This clinical versatility
is very desirable in today’s dental practices where multidisciplinary
treatments are becoming increasingly common.
Check here more “chinadental supplier”.
Related articles:

评论
发表评论